What your Home is telling you
Your home’s foundation is its unsung hero, the bedrock upon which your entire dwelling rests. But like any hero, it’s susceptible to wear and tear, and sometimes, those battles leave visible scars – cracks. While some cracks are benign, others are serious warning signs that your foundation needs immediate attention. Learning to decipher these cracks can save you from costly repairs and potential structural damage.
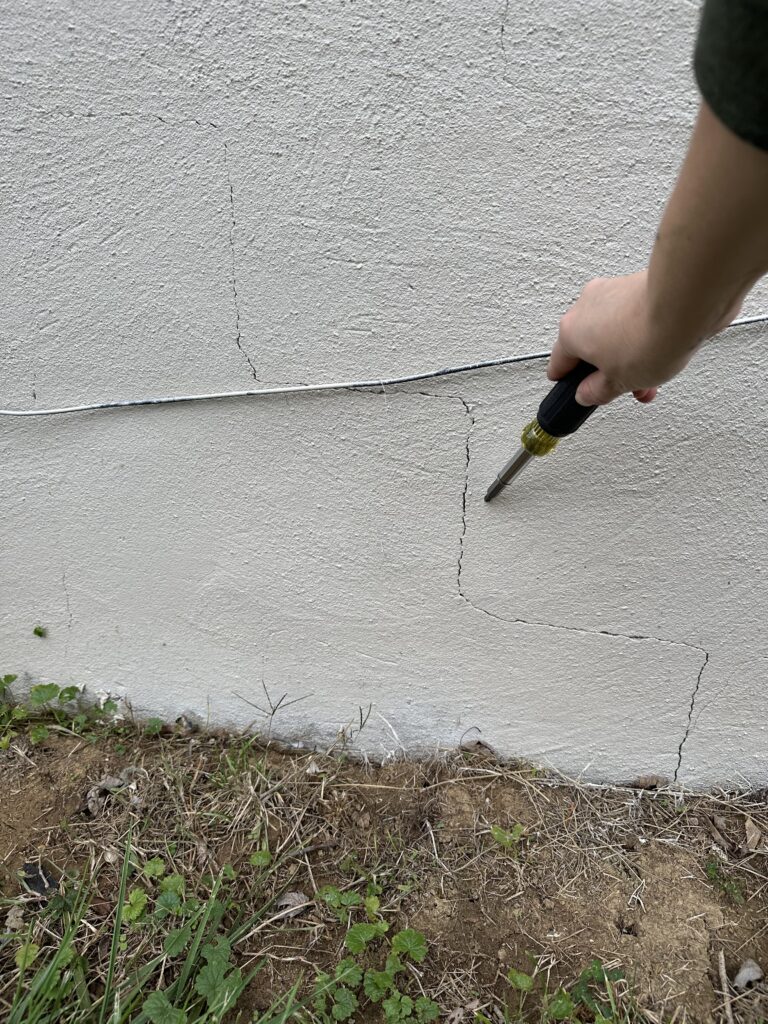

The Anatomy of a Crack: What Type Are We Talking About?
Before we dive into what cracks indicate, let’s understand the different types you might encounter:
Hairline Cracks: These are thin, often barely visible cracks, usually less than 1/16 inch wide.
Vertical Cracks: These run straight up and down.
Horizontal Cracks: These run parallel to the ground.
Diagonal (or 45-degree) Cracks: These run at an angle.
Stair-Step Cracks: These follow the mortar joints of brick or block foundations.
Wide Cracks: Cracks that are wider than 1/4 inch.
Decoding the Messages: What Do These Cracks Mean?
Now, let’s interpret the messages your foundation is sending:
Hairline Cracks (Vertical or Random): Often caused by normal concrete shrinkage during curing. These are usually not a cause for major concern, especially if they remain stable.
Action: Monitor them for changes in width or length. Seal them to prevent water intrusion.
Vertical Cracks: Can be caused by settling, especially if they appear shortly after construction. Minor vertical cracks can also be due to concrete shrinkage.
Action: Monitor for widening. If they widen or are accompanied by other signs of distress, consult a foundation specialist.
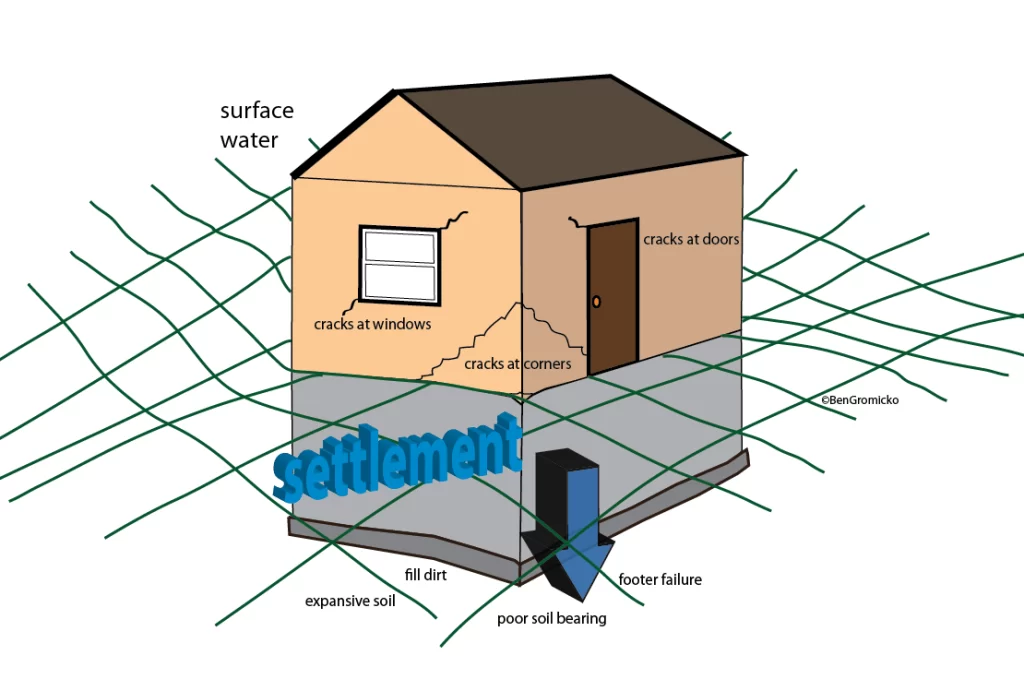
Horizontal Cracks: These are a serious red flag. They often indicate significant lateral pressure from soil pushing against the foundation wall. This pressure can be caused by expansive clay soil, hydrostatic pressure (water buildup), or frost heave.
Action: Immediate professional evaluation is crucial. Horizontal cracks can lead to bowing or collapsing foundation walls.
Diagonal (45-degree) Cracks, ypically indicate foundation settling or differential settling (uneven settling). This can be caused by soil movement, poor soil compaction, or drainage issues.
Action: Monitor for changes. If they widen or are accompanied by other signs of distress, consult a foundation specialist.
Stair-Step Cracks, almost always indicate foundation settling, particularly in brick or block foundations. The stair-step pattern follows the weak points in the mortar joints. These cracks can indicate significant structural movement if they are larger than 1/4″.
Wide Cracks (Any Direction): Wide cracks, regardless of orientation, are a serious sign of foundation distress. They indicate significant movement and potential structural damage. These are larger than 1/4″.
Other Warning Signs to Watch For:
In addition to cracks, be aware of these other signs of potential foundation problems:
- Doors and windows that stick or are difficult to open or close.
- Uneven floors.
- Gaps between walls and ceilings or floors.
- Bowing or leaning walls.
- Water intrusion in the basement or crawlspace.
The Importance of Professional Evaluation:
While this guide can help you understand the basics of foundation cracks, it’s crucial to remember that a professional foundation specialist should always be consulted for a thorough evaluation. They have the expertise to accurately assess the severity of the damage and recommend the appropriate repairs.
Prevention is Key:
To minimize the risk of foundation problems, consider these preventive measures:
- Ensure proper drainage around your home.
- Maintain consistent soil moisture levels.
- Avoid planting trees too close to your foundation.
- Regularly inspect your foundation for signs of damage.
By understanding the language of foundation cracks, you can take proactive steps to protect your home and ensure its long-term stability.

